AIR GAP TRANSDUCERS

The air gap transducers from MC-monitoring are state-of-the-art sensors, engineered with cutting-edge technology to meet the demanding needs of various industrial applications. With over a decade of expertise, MC-monitoring's air gap transducers are trusted and installed in major hydro power plants around the world. Our continuous drive for performance has led to the successful development of sensors for variable speed pumps and generators, wind turbines, and other critical machinery, like ring motors for gearless mill drives. Notably, our high-temperature models are designed to operate in extreme conditions, withstanding temperatures up to 180°C.
Key features
- Wide Range of Reading Distance: Capable of measuring distances between 1mm to 65mm, depending on the sensor type.
- Detachable Sensor: Equipped with three available coaxial/triaxial connectors for easy routing through ventilation holes.
- FPGA Processing and Linearisation: Ensures greater accuracy and stability.
- Active Temperature Compensation: Provides better stability in varying conditions.
- Magnetic Field Resistance: Designed to function efficiently in strong magnetic fields.
- Versatile Outputs: Includes two 2-10V outputs for minimum gap and pole profile, plus one configurable 4-20mA output.
- High-Temperature Tolerance: Certain models are designed to operate at temperatures up to 180°C, making them ideal for harsh environments.
Description
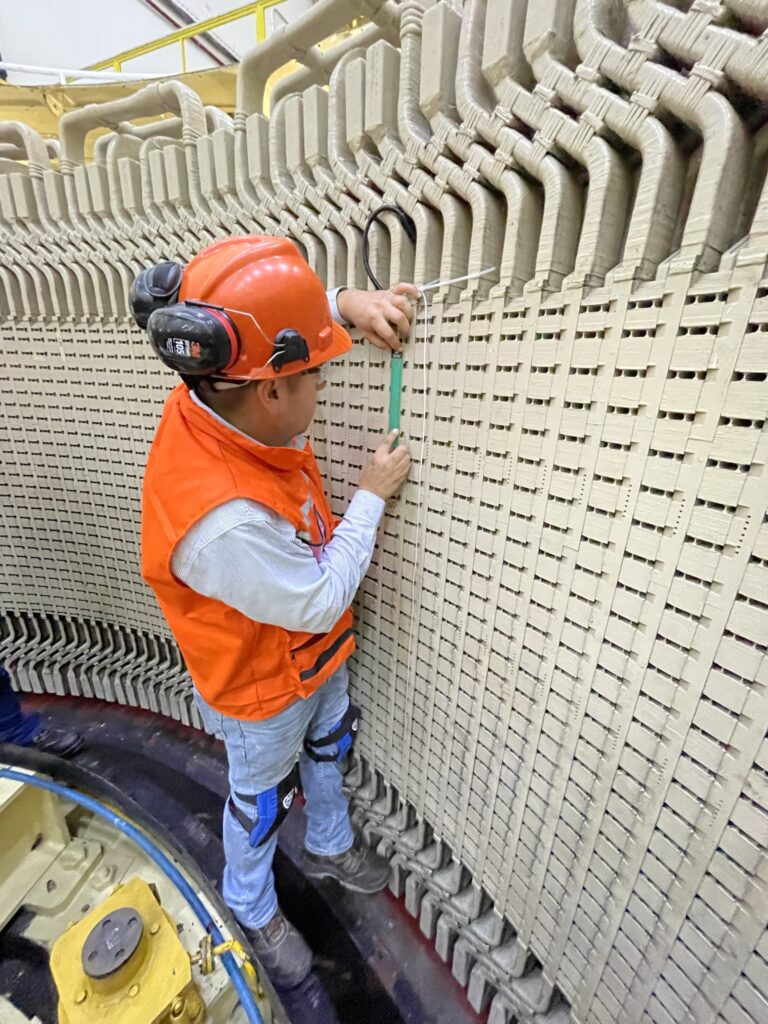
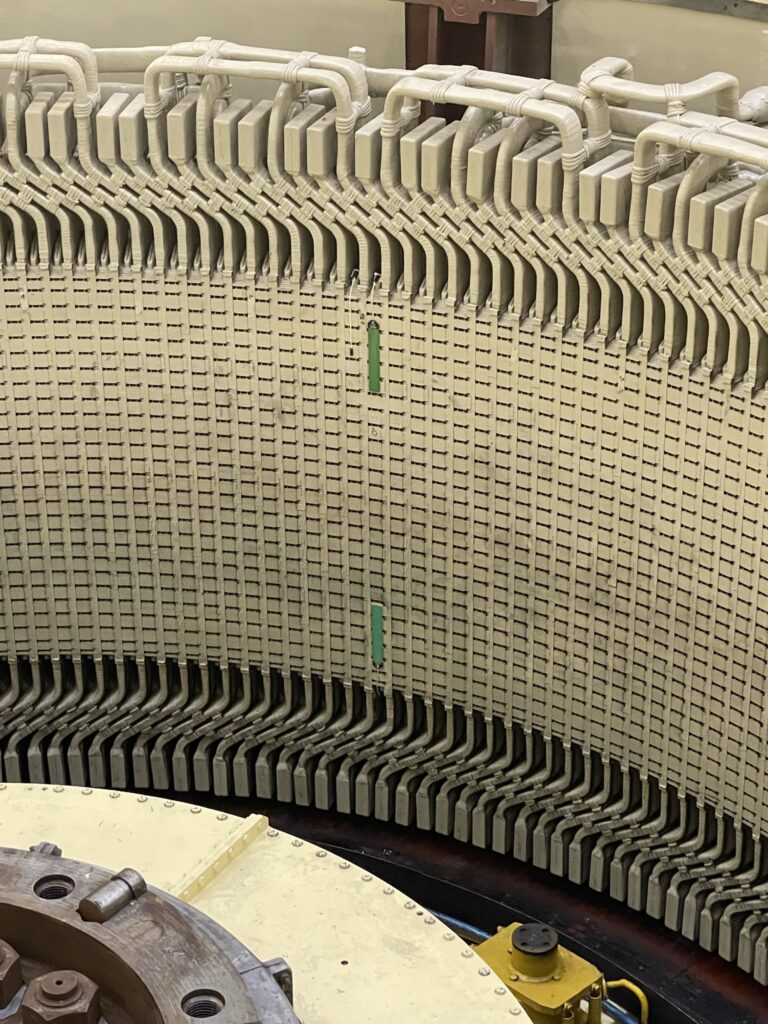
Dynamic air gap monitoring of generators and motors involves measuring the distance between rotor poles and the stator while in operation. MC-monitoring’s AGT range of air gap sensors use a non-contact capacitive technique, offering accurate displacement measurement from the sensor face to a metal target. The capacitive technique's advantage in generator and motor applications is its high immunity to magnetic fields. The AGT series provides high resolution and relative insensitivity to different metal target materials.
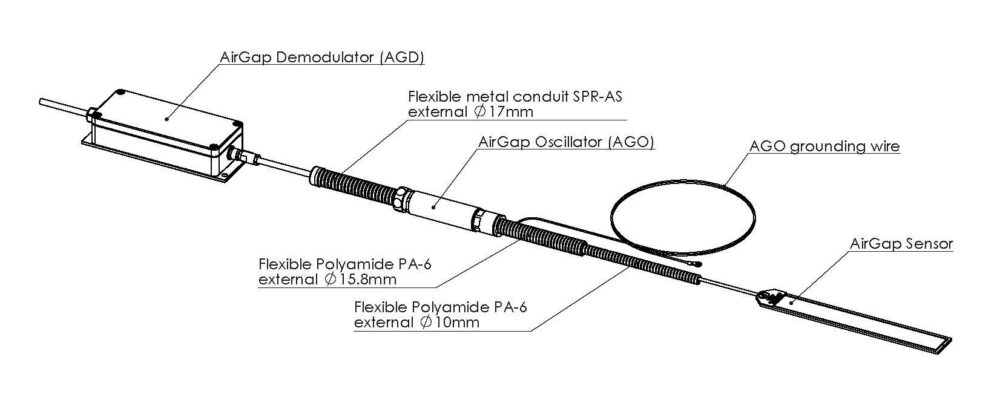
Components of a Typical Capacitive Air Gap Transducer (AGT)
- Sensor (AGS): Designed for installation on the stator wall of generators and motors, suitable for long life cycles in harsh environments and strong magnetic fields.
- Oscillator (AGO): Works in conjunction with the sensor to ensure accurate measurements.
- Demodulator (AGD): Processes signals with digital technology and high-performance noise rejection filters, allowing for precise linearization, stable measurements, and minimal sensitivity to noise. It features three signal outputs:
- MinGap voltage (V)
- Pole Profile voltage (V)
- Pole Profile or MinGap current (mA)
Understanding Signal Outputs
The signal outputs from the demodulator provide critical information for monitoring and analyzing the generator's/motor’s performance:
- MinGap Voltage (V): Indicates the minimum gap distance measured, useful for detecting the closest approach of rotor poles to the stator.
- Pole Profile Voltage (V): Represents the profile of the rotor poles as they pass by the sensor, helping to assess the shape and uniformity of the poles.
- Pole Profile or MinGap Current (mA): Configurable to either pole profile or minimum gap current output, this signal provides a current-based measurement option that can be integrated into various monitoring systems.
All outputs are galvanically isolated, and the current output is factory-set on Pole Profile. The industrial metal housing of the demodulator ensures durability in harsh environments. The FPGA-based demodulators allow highly repeatable and stable measurements.
Optimal Number of Sensors
To achieve the best measurement resolution, we recommend the following sensor configurations based on the hydro generator size:
- Generators with a diameter of less than 6 meters: Install 4 sensors on the driven side and 4 on the non-driven side.
- Generators with a diameter of 6 to 12 meters: Install 8 sensors on the upper side and 8 on the lower side.
- Generators with larger diameters: Install 12 to 16 sensors per side.
Installation
The air gap sensors are typically glued to the stator core laminations inside the air gap, beneath a ventilation hole. This placement ensures that the sensor surface is always completely covered by the rotor pole surface, providing accurate measurements.
Monitoring solutions
Applications
Available models
Type (3G) | AGS (p/n) | AGO (p/n) | AGD (p/n) | Measuring range [MM] | Output range |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
min | max | |||||
| AGT-212 | (04.212.100 M4) | (04.xxx.400 M3) | ||||
| AGT-212 | (04.212.100 M4) | |||||
| AGT-212 | ||||||
| AGT-520 | ||||||
| AGT-525 | ||||||
| AGT-525 | ||||||
| AGT-550 | ||||||
| AGT-550 | ||||||
| AGT-550 | ||||||
| AGT-550MX | ||||||
| AGT-525 | (04.2xx.400 M3) | |||||
| AGT-212 | ||||||
| AGT-212 | (04.3xx.400 M3) | |||||
High Temperature Applications
Type (3G) | AGS (p/n) | AGO (p/n) | AGD (p/n) | Measuring range [MM] | Output range |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
min | max | |||||
| AGT-105HT | (04.3xx.400 M3) | |||||
| AGT-212HT | ||||||
| AGT-212HT | ||||||
Downloads
LET'S KEEP IN TOUCH
Sign up to receive our newsletters