AIR GAP MONITORING

Description
Large, low-speed hydro generators have a very small ratio between the stator bore diameter and the air gap, which makes it impossible to center the elements perfectly during the assembly process. As a result, the machines operate with a small but relevant misalignment.
Faults on the poles can lead to a considerable unbalance of the magnetic attraction forces, which also leads to significant misalignment, vibration, and additional losses.
It is therefore important to assess the following parameters: misalignment; minimum and maximum air gaps; stator and rotor shape; magnetic flux of each pole; and, above all, to check the machine’s mechanical trend, to ensure safe operation and avoid serious damage.
Typical faults detections
- Rotor-to-stator rub
- Pole mechanical instability
- Loss of operating efficiency
- Magnetic unbalance
- Thermal hotspots
Typical installation
Depending on the stator size, between 4 to 16 airgap sensors installed uniformly around the stator core
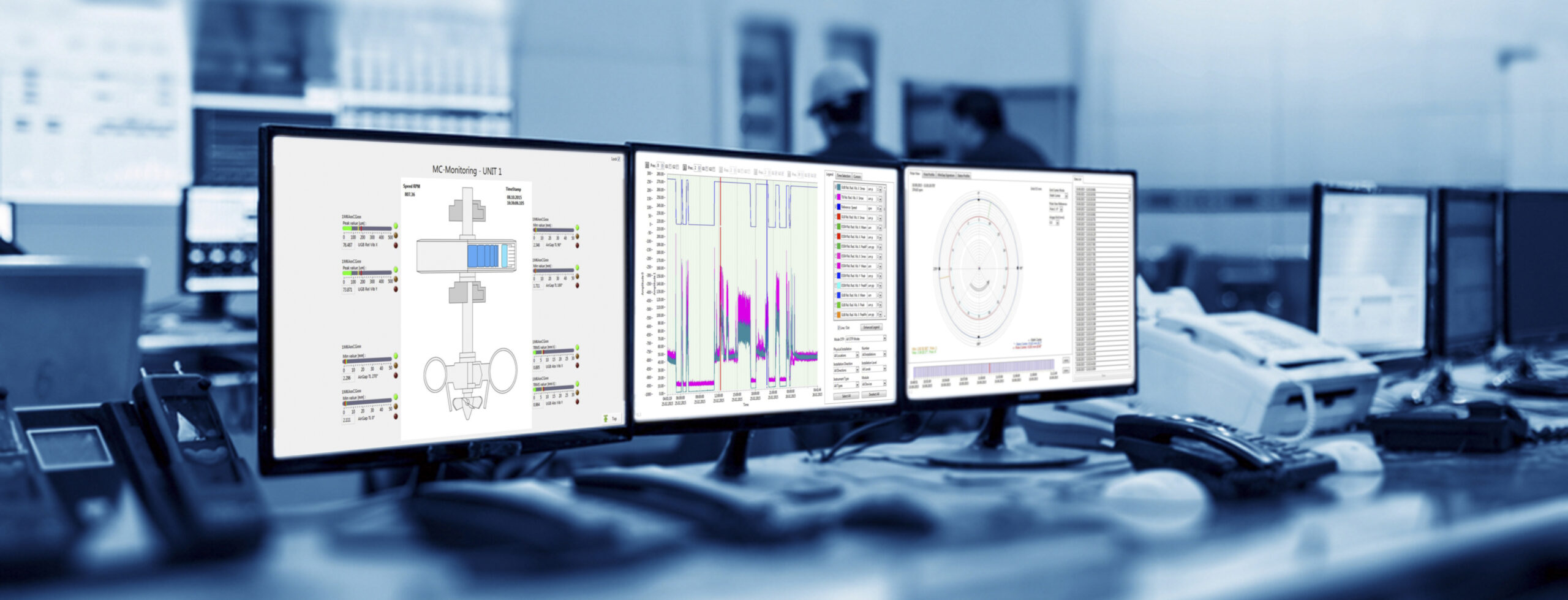
Monitoring parameters
- MPS: Minimum gap per revolution
- CMS: Pole profile, stator shape, rotor shape, stator and rotor center position, minimum gap position, pole stability
Related sensors
LET'S KEEP IN TOUCH
Sign up to receive our newsletters